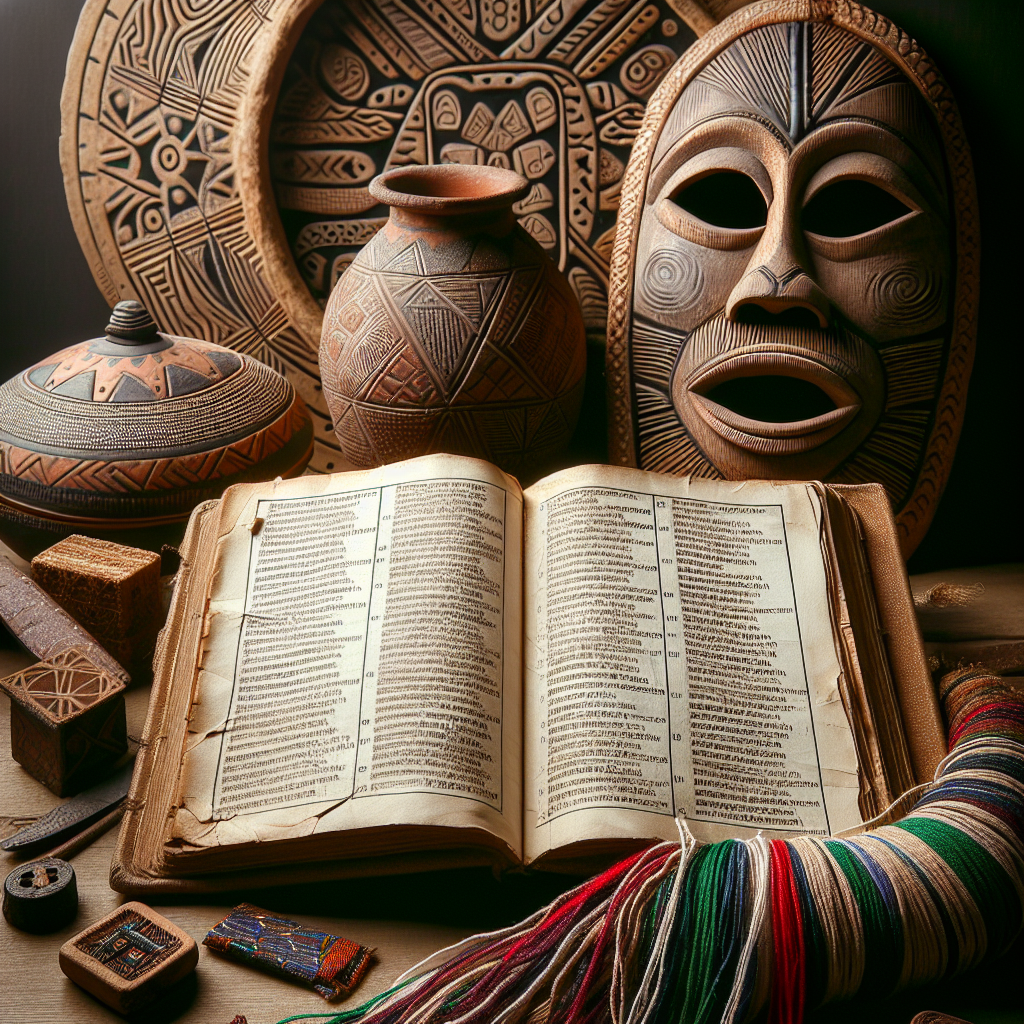
Nigeria, often referred to as the “Giant of Africa,” is a country rich in culture and tradition. One significant aspect of Nigerian culture is religion, which plays a crucial role in shaping the beliefs and practices of the people. The religious landscape of Nigeria is diverse, with Christianity and Islam being the two dominant religions, while traditional African religions also hold a significant place in the lives of many Nigerians.
Christianity was introduced to Nigeria by European missionaries in the 19th century and has since grown to become the largest religion in the country. Nigerian Christians are known for their fervent faith and vibrant worship services, with a significant percentage of the population regularly attending church services and participating in various religious activities. Christianity has influenced many aspects of Nigerian culture, including music, art, and literature, and has played a crucial role in shaping the social and political landscape of the country.
Islam, on the other hand, was brought to Nigeria through trade and conquest in the 11th century and has also become a prominent religion in the country, especially in the northern region. Nigerian Muslims are known for their devotion to the five pillars of Islam, including daily prayers, fasting during Ramadan, giving alms to the poor, and making the pilgrimage to Mecca. Islam has also influenced Nigerian culture, particularly in the areas of fashion, architecture, and cuisine, with many Nigerians incorporating Islamic traditions into their daily lives.
In addition to Christianity and Islam, traditional African religions also play a significant role in Nigerian culture. These religions are based on the worship of various deities, spirits, and ancestors, and involve practices such as divination, sacrifices, and ceremonies. Many Nigerians maintain a dual religious identity, practicing both Christianity or Islam and traditional African religions, depending on the situation or occasion. Traditional African religions also play a vital role in cultural ceremonies and festivals, such as weddings, funerals, and annual celebrations.
The role of religion in Nigerian traditions and beliefs is complex and multifaceted, with each religion contributing to the cultural diversity and richness of the country. Religion serves as a guide for moral values, social norms, and personal identity, shaping the way Nigerians interact with one another and perceive the world around them. Through religion, Nigerians find meaning, purpose, and a sense of community, fostering a strong sense of unity and solidarity among the people.
In conclusion, religion plays a pivotal role in Nigerian traditions and beliefs, shaping the cultural, social, and political landscape of the country. Christianity, Islam, and traditional African religions each contribute to the diverse tapestry of Nigerian culture, providing a sense of identity, meaning, and connection to the people. As Nigeria continues to evolve and grow, religion will undoubtedly remain a central and enduring aspect of the country’s cultural heritage.